Health insurance marketplace, a term that might sound intimidating, actually represents a powerful tool for navigating the complex world of healthcare. Imagine a one-stop shop where you can compare different health insurance plans, explore your options, and find the best fit for your needs and budget.
That’s exactly what a health insurance marketplace offers, and it’s become a vital resource for millions of Americans seeking affordable and comprehensive coverage.
Established under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), these marketplaces aim to simplify the process of finding health insurance by providing a platform where individuals can compare plans side-by-side. Whether you’re self-employed, part of a small business, or simply looking for a more flexible and affordable option, understanding how health insurance marketplaces work can empower you to make informed decisions about your healthcare.
Introduction to Health Insurance Marketplaces
Navigating the world of health insurance can feel like a maze, but health insurance marketplaces are designed to make the process easier and more transparent. These online platforms serve as a one-stop shop for comparing and purchasing health insurance plans.
The Purpose and Function of Health Insurance Marketplaces
Health insurance marketplaces act as a centralized hub for individuals and families to explore and select health insurance plans that meet their needs and budget. They provide a platform where you can:
- Compare plans from different insurance companies side-by-side.
- Learn about plan details, including coverage, costs, and deductibles.
- Apply for financial assistance, such as tax credits, to reduce the cost of premiums.
- Enroll in a plan that meets your eligibility requirements.
These marketplaces streamline the process of finding and obtaining health insurance, eliminating the need to contact multiple insurance companies individually.
The Historical Context of Health Insurance Marketplaces in the United States
The concept of health insurance marketplaces gained prominence with the Affordable Care Act (ACA), also known as Obamacare, enacted in The ACA aimed to expand health insurance coverage and make it more affordable for millions of Americans. The law established state-based marketplaces, known as Health Insurance Marketplaces or Exchanges, to facilitate the purchase of health insurance plans.
These marketplaces were designed to:
- Offer a wider range of health insurance plans, including plans from both private and public insurers.
- Provide subsidies and tax credits to eligible individuals and families to make coverage more affordable.
- Offer standardized plans with clear benefits and costs, making it easier for consumers to compare options.
Since their inception, health insurance marketplaces have become a significant aspect of the health insurance landscape in the United States, offering a vital resource for individuals and families seeking affordable and comprehensive health coverage.
The Key Benefits of Using a Health Insurance Marketplace
Using a health insurance marketplace offers several advantages:
- Convenience and Accessibility:Marketplaces provide a convenient and accessible platform for comparing plans, applying for financial assistance, and enrolling in coverage, all from the comfort of your home or on the go.
- Transparency and Choice:Marketplaces offer a transparent comparison of plans, allowing you to see side-by-side details about coverage, costs, and deductibles, giving you the freedom to choose the plan that best fits your needs and budget.
- Financial Assistance:Marketplaces offer tax credits and subsidies to eligible individuals and families, reducing the cost of premiums and making health insurance more affordable.
- Expert Guidance:Marketplaces often provide access to certified enrollment assistants who can guide you through the process and answer your questions, ensuring you understand your options and make informed decisions.
Types of Health Insurance Plans Available
Health insurance marketplaces offer a variety of plans to suit different needs and budgets. Understanding the different types of plans available is crucial to choosing the right coverage for you and your family.
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs)
HMOs are known for their lower premiums, but they have strict rules about who you can see for care. You’ll need to choose a primary care physician (PCP) within the HMO’s network, and you’ll generally need a referral from your PCP to see specialists.
- Lower Premiums:HMOs typically have lower monthly premiums compared to other plan types, making them a cost-effective option for some individuals and families.
- Limited Network:You can only receive care from doctors and hospitals within the HMO’s network. This means you may have fewer choices when it comes to selecting your healthcare providers.
- Referral Requirements:You usually need a referral from your PCP to see a specialist. This can sometimes lead to delays in receiving care.
- Lower Out-of-Pocket Costs:HMOs often have lower copayments and deductibles compared to other plans.
Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs)
PPOs offer more flexibility than HMOs, allowing you to see doctors and hospitals outside of the network, although you’ll pay more for out-of-network care.
- Larger Network:PPOs typically have a wider network of doctors and hospitals than HMOs, giving you more choices for healthcare providers.
- No Referral Requirements:You don’t need a referral from your PCP to see a specialist.
- Higher Premiums:PPOs generally have higher monthly premiums than HMOs due to the wider network and greater flexibility.
- Higher Out-of-Pocket Costs:PPOs often have higher copayments and deductibles compared to HMOs.
- Out-of-Network Coverage:PPOs cover out-of-network care, but at a higher cost. You’ll typically pay a higher coinsurance percentage and a larger deductible for out-of-network services.
Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs)
EPOs are similar to HMOs in that they require you to choose a PCP within the network and generally need referrals for specialist care. However, EPOs do not cover out-of-network care, except in emergencies.
- Limited Network:EPOs have a limited network of doctors and hospitals, similar to HMOs.
- Referral Requirements:EPOs generally require referrals from your PCP to see specialists.
- No Out-of-Network Coverage:EPOs do not cover out-of-network care, except in emergency situations.
- Lower Premiums:EPOs typically have lower premiums than PPOs, but higher premiums than HMOs.
Point-of-Service (POS) Plans
POS plans combine features of HMOs and PPOs. You’ll choose a PCP within the network, but you have the option to see out-of-network providers, although you’ll pay more for out-of-network care.
Navigating the health insurance marketplace can feel like a maze, but remember, it’s not just about today’s needs. Planning for the future is crucial, and that’s where Long-term care insurance comes in. This type of insurance helps cover the costs of long-term care services, which can be expensive, and gives you peace of mind knowing you’re prepared for potential future needs.
So, while you’re exploring your health insurance options, don’t forget to consider the long-term care aspect – it could be a valuable addition to your overall financial strategy.
- Combined Features:POS plans combine aspects of HMOs and PPOs, offering some flexibility while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
- PCP Requirement:You’ll need to choose a PCP within the POS network.
- Out-of-Network Coverage:POS plans allow you to see out-of-network providers, but you’ll pay a higher deductible and coinsurance for these services.
- Moderate Premiums:POS plans typically have moderate premiums compared to HMOs and PPOs.
Navigating the Marketplace Platform
The Health Insurance Marketplace website is designed to be user-friendly and intuitive. It provides a variety of tools and resources to help you find the right health insurance plan. Let’s explore how to navigate the website and access these helpful resources.
Navigating the Marketplace Website
The Health Insurance Marketplace website has a clear and simple layout, making it easy to find the information you need. The website is typically organized with a menu bar at the top, providing access to key sections like:
- Home:This section provides an overview of the Marketplace, its purpose, and key features.
- Find a Plan:This section allows you to search for health insurance plans based on your individual needs and circumstances.
- Enroll:This section guides you through the process of applying for coverage and enrolling in a plan.
- Manage My Account:This section allows you to manage your account information, update your contact details, and access your plan documents.
- Help and Support:This section provides access to FAQs, contact information, and other resources to assist you with any questions or concerns.
Using Marketplace Tools and Resources
The Marketplace website offers a variety of tools and resources to help you find the right plan. These include:
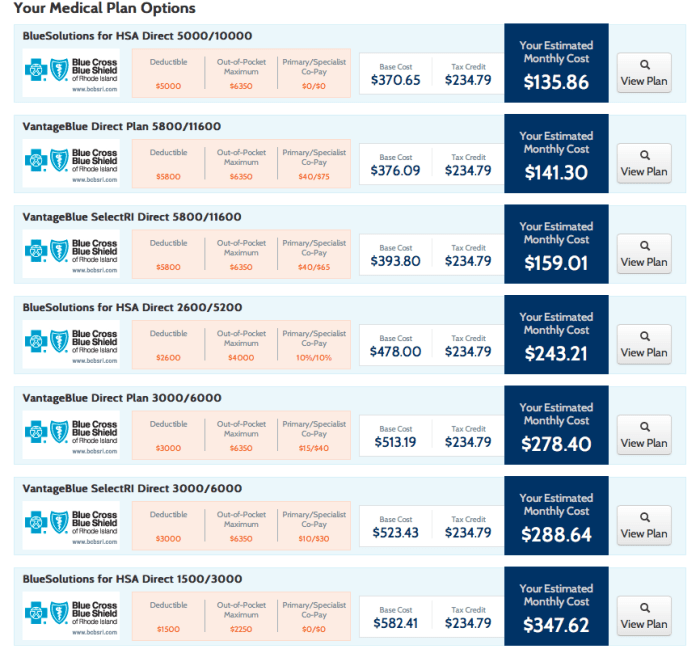
- Plan Comparison Tool:This tool allows you to compare different health insurance plans side-by-side, based on factors like premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and coverage benefits.
- Eligibility Checker:This tool helps you determine if you qualify for financial assistance to help pay for your premiums. It considers factors like income, family size, and age.
- Plan Finder:This tool helps you narrow down your search for plans based on your specific needs and preferences. You can filter plans by coverage level, network, and other criteria.
- Health Insurance Glossary:This resource provides definitions of common health insurance terms and concepts, helping you understand the jargon associated with health insurance.
Applying for Coverage and Enrolling in a Plan
The process of applying for coverage and enrolling in a plan is straightforward:
- Create an Account:You’ll need to create an account on the Marketplace website to access the application process.
- Provide Personal Information:You’ll be asked to provide personal information, including your name, address, Social Security number, income, and family size.
- Compare Plans:Use the Marketplace tools and resources to compare different health insurance plans based on your needs and budget.
- Select a Plan:Once you’ve chosen a plan, you’ll need to submit your application and enroll in the plan.
- Review and Confirm:Before finalizing your enrollment, review your application and confirm all the information is accurate.
Important Note:You may be able to enroll in a health insurance plan outside of the Open Enrollment period if you qualify for a Special Enrollment Period. These periods are available for certain life events, such as getting married, having a baby, or losing other health insurance coverage.
Factors Influencing Plan Selection: Health Insurance Marketplace
Choosing the right health insurance plan is a crucial decision that can significantly impact your financial well-being and access to healthcare. Several factors come into play when making this choice, requiring careful consideration and a comprehensive understanding of your needs and priorities.
Coverage and Benefits
It’s essential to compare plans based on the coverage they provide, ensuring it aligns with your individual needs and potential healthcare requirements. The breadth of services covered by a plan, including preventive care, hospitalization, prescription drugs, and mental health services, varies significantly.
For example, some plans may offer extensive coverage for preventive care, while others may have limited coverage for certain medications.
Cost and Premiums
Cost is a major factor in plan selection. Premiums, deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance are key components that influence the overall cost of your health insurance.
Premiums are the monthly payments you make for your health insurance coverage. Deductibles are the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Copayments are fixed amounts you pay for specific services, while coinsurance is a percentage of the cost you share with your insurer.
Network and Provider Availability
The network of healthcare providers included in your health insurance plan is crucial. You need to ensure that your preferred doctors, hospitals, and specialists are in the plan’s network.
Out-of-network care can be significantly more expensive, and you may face higher costs or even have to pay for the entire service yourself.
Personal Health Needs and Financial Situation
Your individual health needs and financial situation are key factors in plan selection. If you have pre-existing conditions or anticipate needing frequent healthcare services, you’ll need a plan with comprehensive coverage. Your financial situation will determine how much you can afford to pay in premiums and out-of-pocket expenses.
For example, if you have a chronic illness, you’ll need a plan that covers the necessary treatments and medications. If you’re on a tight budget, you’ll need to find a plan with affordable premiums and low out-of-pocket costs.
Financial Assistance and Subsidies
Navigating the complexities of health insurance can be overwhelming, but the good news is that financial assistance is available to help make coverage more affordable. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) provides subsidies and tax credits to individuals and families who meet certain income requirements.
These programs can significantly reduce your monthly premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
Types of Financial Assistance
Financial assistance is available in two primary forms:
- Premium Tax Credits: These credits directly reduce the amount of taxes you owe, making your health insurance more affordable. They are available to individuals and families who meet specific income requirements and purchase coverage through the Marketplace.
- Cost-Sharing Reductions: These subsidies lower your out-of-pocket costs, such as deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance. They are available to individuals and families with lower incomes who purchase a Silver plan through the Marketplace.
Eligibility Criteria for Subsidies and Tax Credits
Eligibility for financial assistance is based on your household income, household size, and location. You can use the Marketplace’s online tool to determine your eligibility and estimate your potential savings.
Examples of Financial Assistance Impact
Here are some real-world examples of how financial assistance can impact the cost of health insurance:
- Scenario 1:A single individual earning $30,000 per year might qualify for a premium tax credit that reduces their monthly premium by $100. This can significantly impact their ability to afford quality health insurance.
- Scenario 2:A family of four with an income of $50,000 per year might qualify for both premium tax credits and cost-sharing reductions. This can dramatically reduce their overall healthcare expenses.
Open Enrollment and Special Enrollment Periods

The open enrollment period is a designated time frame when individuals can sign up for or change their health insurance plans through the marketplace. It’s a crucial period for ensuring you have health insurance coverage for the upcoming year.
Open Enrollment Period
The open enrollment period for marketplace plans typically runs from November 1st to January 15th each year. During this time, you can:* Enroll in a health insurance plan for the first time.
- Change your existing plan.
- Drop your coverage entirely.
- Sign up for coverage that starts on January 1st of the following year.
Special Enrollment Periods
There are specific situations where you can enroll or make changes to your health insurance plan outside of the open enrollment period. These are known as special enrollment periods (SEPs).
Types of Special Enrollment Periods
- Life Events:Significant life changes, such as marriage, divorce, birth of a child, adoption, or loss of job-based coverage, can trigger an SEP.
- Income Changes:If your income drops below a certain threshold, you may qualify for a SEP to enroll in a more affordable plan.
- Moving to a New Coverage Area:If you move to a different state or county, you may have access to different plans, and an SEP can allow you to switch.
- Changes in Your Household Size:If someone joins or leaves your household, you may be eligible for an SEP to adjust your coverage.
- Medicaid or CHIP Eligibility:If you become eligible for Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP), you can enroll through an SEP.
Navigating Open Enrollment and Special Enrollment Periods, Health insurance marketplace
- Stay Organized:Keep track of important dates, deadlines, and documentation related to your health insurance.
- Compare Plans Carefully:Use the marketplace’s tools to compare plans based on your needs and budget.
- Seek Guidance:If you have questions or need assistance, contact the marketplace’s customer support or a certified enrollment assister.
- Act Promptly:Don’t wait until the last minute to enroll or make changes to your plan. This can lead to missed deadlines and potential gaps in coverage.
Understanding Your Coverage and Benefits
Once you’ve selected a health insurance plan from the marketplace, it’s crucial to understand the details of your coverage and how to utilize your benefits effectively. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions about your healthcare and ensures you receive the maximum value from your chosen plan.
Types of Coverage Included in Health Insurance Plans
Health insurance plans typically include a variety of coverage categories, each addressing different aspects of healthcare needs.
- Essential Health Benefits:These are ten essential health benefits mandated by the Affordable Care Act, covering a wide range of healthcare services, including preventive care, hospitalization, prescription drugs, maternity and newborn care, mental health and substance use disorder services, and more.
- Preventive Care:This includes screenings, immunizations, and other services aimed at preventing illness and promoting overall health. Many plans cover these services without requiring a copay or deductible.
- Ambulatory Patient Services:This category encompasses healthcare services provided outside of a hospital setting, such as doctor’s visits, outpatient surgery, and lab tests.
- Emergency Services:Plans typically cover emergency room visits and other urgent care services, regardless of whether the provider is in your network.
- Hospitalization:This includes coverage for inpatient care, such as surgery, intensive care, and overnight stays.
- Prescription Drugs:Most plans include a formulary, a list of covered prescription medications. You may have to pay a copay or deductible for these drugs.
- Maternity and Newborn Care:This coverage includes prenatal care, childbirth, and postpartum care for both mother and baby.
- Mental Health and Substance Use Disorder Services:Plans cover mental health services, including counseling, therapy, and medication.
- Rehabilitative Services and Devices:This category includes coverage for services like physical therapy, occupational therapy, and assistive devices.
- Laboratory Services:Coverage for lab tests, including blood work and diagnostic tests.
Accessing Healthcare Services Under a Marketplace Plan
Understanding how to access healthcare services under your marketplace plan is crucial for a smooth and efficient healthcare experience.
- Choosing a Provider:Most marketplace plans have a network of providers, which are healthcare professionals and facilities that have agreed to provide services at a negotiated rate. It’s important to select providers within your network to maximize your benefits.
- Obtaining Pre-Authorization:For certain services, such as elective surgeries or specialized treatments, you may need to obtain pre-authorization from your insurance company. This ensures that the service is covered by your plan and helps avoid unexpected costs.
- Presenting Your Insurance Card:When you receive healthcare services, you will need to present your insurance card to the provider. This card contains your policy information and allows the provider to verify your coverage and billing details.
- Understanding Copayments and Deductibles:You may be responsible for paying a copayment or deductible for certain services, depending on your plan. Copayments are fixed amounts you pay at the time of service, while deductibles are a set amount you need to pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in.
- Filing Claims:After receiving healthcare services, you may need to file a claim with your insurance company. This is typically done by the provider on your behalf, but you can also file claims directly if needed.
Understanding and Utilizing Your Benefits
Your health insurance plan comes with a comprehensive benefits booklet or summary of benefits and coverage (SBC) that Artikels your plan’s details.
- Reviewing Your Benefits Booklet:Take the time to thoroughly review your benefits booklet. It contains information about your covered services, deductibles, copayments, out-of-pocket maximums, and other important details.
- Understanding Your Out-of-Pocket Maximum:Your out-of-pocket maximum is the most you’ll have to pay for covered healthcare services in a year. Once you reach this limit, your insurance company will cover 100% of your eligible medical expenses for the rest of the year.
- Utilizing Preventive Care Services:Many plans cover preventive care services, such as screenings and immunizations, at no cost to you. Taking advantage of these services can help prevent health problems and save money in the long run.
- Understanding Your Coverage for Prescription Drugs:Your plan’s formulary lists the covered prescription drugs and their associated copayments or deductibles. If your doctor prescribes a medication that is not on the formulary, you may have to request prior authorization or consider alternative medications.
- Contacting Customer Service:If you have any questions about your coverage or benefits, don’t hesitate to contact your insurance company’s customer service department. They can provide you with detailed information and support.
Consumer Protections and Regulations
The health insurance marketplace is designed to offer a variety of plans and ensure that consumers are protected throughout the process. Federal and state regulations govern the marketplace, ensuring fair practices and consumer rights.
Government Oversight and Regulation
The government plays a crucial role in overseeing the marketplace and ensuring fair practices. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) established the marketplace and implemented regulations to protect consumers. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is responsible for administering the marketplace and enforcing these regulations.
Consumer Rights and Protections
Consumers have various rights and protections when participating in the marketplace.
- Access to Information:Consumers have the right to access clear and concise information about available plans, their costs, and benefits.
- Protection from Discrimination:Health insurance companies cannot discriminate based on health status, gender, or other factors.
- Right to Appeal:Consumers can appeal decisions made by the marketplace or insurance companies.
- Assistance with Enrollment:Navigators and certified application counselors provide free assistance with the enrollment process.
Addressing Potential Issues
Consumers should know how to address potential issues or concerns they may encounter.
- Contact the Marketplace:Consumers can contact the marketplace directly to report issues or seek assistance.
- File a Complaint:Consumers can file complaints with the marketplace or the CMS if they believe their rights have been violated.
- Seek Legal Assistance:In some cases, consumers may need to seek legal assistance to address complex issues or disputes.
Impact of Health Insurance Marketplaces
Health insurance marketplaces have significantly impacted the healthcare system since their inception, transforming the way individuals and families access and pay for health insurance. These marketplaces offer a centralized platform for individuals to compare and enroll in various health insurance plans, creating a competitive environment that has brought about both benefits and challenges.
Impact on Healthcare System
The establishment of health insurance marketplaces has led to notable changes within the healthcare system. These changes can be analyzed by examining their impact on various stakeholders, including consumers, providers, and insurers.
Impact on Consumers
- Increased Choice and Competition:Marketplaces provide consumers with access to a wider selection of health insurance plans from multiple insurers, fostering competition and potentially leading to lower premiums and improved benefits.
- Simplified Enrollment Process:The online platform simplifies the enrollment process, allowing individuals to compare plans, apply for subsidies, and enroll in coverage all in one place. This convenience makes it easier for people to access health insurance.
- Financial Assistance and Subsidies:Marketplaces offer subsidies and tax credits to eligible individuals and families, making health insurance more affordable. These subsidies are based on income levels and help lower out-of-pocket costs.
Impact on Providers
- Increased Patient Pool:Marketplaces can potentially increase the patient pool for providers, particularly those participating in plans offered through the marketplace. This can lead to increased revenue and improved financial stability for providers.
- Challenges in Payment Models:Some providers may face challenges in navigating the complex payment models associated with marketplace plans. These models can differ from traditional fee-for-service arrangements, requiring providers to adapt their billing practices.
Impact on Insurers
- New Market Opportunities:Marketplaces provide insurers with new opportunities to reach a wider customer base. The competitive environment encourages insurers to offer more competitive plans to attract consumers.
- Regulatory Compliance:Insurers must comply with various regulations associated with marketplace participation, including requirements for plan design and coverage. This can add to administrative burdens for insurers.
Conclusion
Navigating the health insurance marketplace can seem overwhelming at first, but with the right tools and resources, it can be a smooth and rewarding experience. Remember, the marketplace is designed to help you find the plan that best meets your individual needs and financial situation.
By taking advantage of the available resources and understanding your options, you can confidently secure the healthcare coverage you deserve.
Essential FAQs
What is the difference between an HMO and a PPO?
An HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) typically requires you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) within the network. You’ll need a referral from your PCP to see specialists. PPOs (Preferred Provider Organizations) offer more flexibility, allowing you to see specialists without a referral, but may have higher out-of-pocket costs for providers outside the network.
Can I get financial assistance to pay for my health insurance?
Yes! The marketplace offers subsidies and tax credits to eligible individuals and families based on income. These subsidies can significantly reduce your monthly premiums.
What if I miss the open enrollment period?
You might qualify for a special enrollment period if you experience a life-changing event, such as getting married, having a baby, or losing your job. These periods allow you to enroll in a plan outside of the regular open enrollment window.